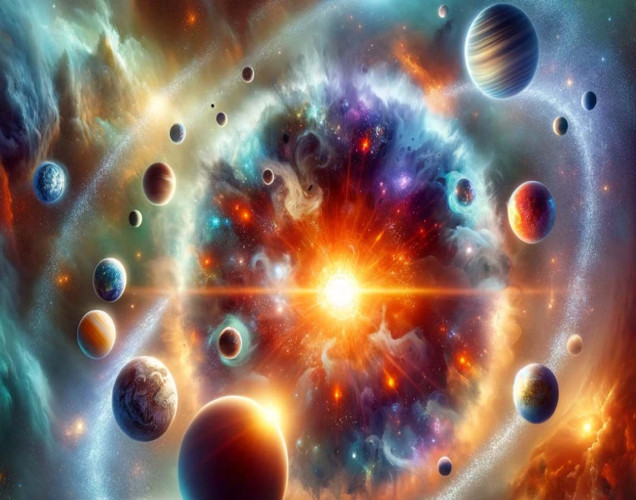
"Twinkle, twinkle, giant star
How I wonder what you are
Up above the world so high
Shining secrets in the sky."
Have you ever wondered how the universe started?
The Big Bang Theory is a fun and fascinating idea that helps us understand the very beginning of everything! Let’s dive into this amazing story of our universe's birth and how it led to the formation of stars, galaxies, and planets.
What is the Big Bang Theory?
The Big Bang Theory is a way scientists explain how the universe began. Imagine everything you see in the sky – stars, planets and galaxies – all squished into a tiny, hot and dense point. About 13.8 billion years ago, this point exploded and our universe started expanding. This big explosion is called the Big Bang.
1. *Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR)*
Scientists discovered a special kind of light called the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. This light is like the leftover glow from the Big Bang. It does everywhere in the universe and helps scientists know that the Big Bang really happened.
2. *Redshift of Galaxies*
When scientists look at galaxies far away, they see that these galaxies are moving away from us. This is called redshift. It’s like when a balloon gets bigger as you blow air into it. The redshift shows that the universe is still expanding, just like it did after the Big Bang.
3. *Lots of Hydrogen and Helium*
Right after the Big Bang, the universe was mostly made up of two elements: hydrogen and helium. Scientists see lots of hydrogen and helium in the universe today, just like the Big Bang Theory predicts.
How Did Stars and Galaxies Form?
After the Big Bang, the universe started growing really fast. This is called inflation. As it got bigger, it also cooled down. When it was cool enough, tiny particles came together to form atoms. These atoms clumped together to form stars.
Stars grouped together to form galaxies. A galaxy is a huge collection of stars, planets, and dust, all held together by gravity. Our solar system, with the Sun and planets, is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way.
How Did Planets Form?
Inside galaxies, dust and gas clumped together to form stars and planets. Our own solar system formed from a big cloud of gas and dust. Over time, this cloud collapsed under its own gravity to form the Sun. The leftover gas and dust around the Sun stuck together to form planets, moons, and other objects.
Earth, the planet we live on, is one of these planets. It formed about 4.5 billion years ago, long after the Big Bang. The same process that made Earth also made all the other planets in our solar system.
Why is the Big Bang Theory Important?
The Big Bang Theory helps us understand where we come from and how everything around us was made. It’s like learning the universe’s origin story. This theory also makes scientists curious to learn more about other mysteries, like dark matter and dark energy.
"Big Bang burst and stars were born, Galaxies danced, the sky adorned. Planets formed and life took flight, in the universe's endless night."
Conclusion
The Big Bang Theory is an exciting way to think about the beginning of the universe. It teaches us that everything we see today started from a tiny, powerful explosion billions of years ago. From this explosion came stars, galaxies, and planets, including Earth. As we learn more, we can discover even more amazing things about our universe. Keep looking up at the stars and wondering – there’s so much to explore!